Understand Scrapoxy
Architecture
Scrapoxy consists of 4 parts:
the master, which routes requests to proxies;
the manager, which starts and stops proxies;
the commander, which provides a REST API to receive orders;
the gui, which connects to the REST API.
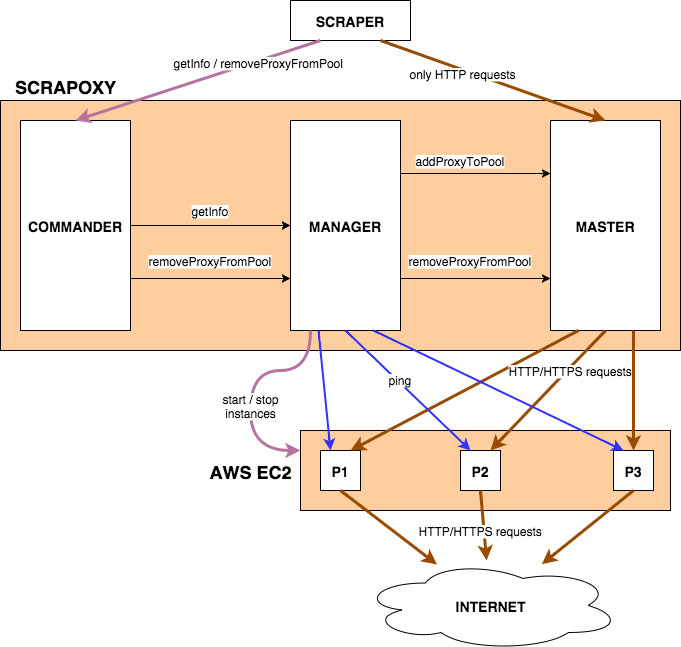
When Scrapoxy starts, the manager starts a new instance (if necessary), on the cloud.
When the scraper sends a HTTP request, the manager starts all others proxies.
Requests
Can Scrapoxy relay HTTPS requests ?
Yes. There is 2 modes:
Mode A: HTTPS CONNECT with MITM (Man-In-The-Middle)
This mode is for unsecure browser like PhantomJS. It allow Scrapoxy to decrypt SSL and override HTTP headers (like User-Agent).
This solution can trigger some SSL alerts.
Mode B: HTTPS CONNECT without MITM
This mode is for secure browser. It doesn’t allow Scrapoxy to override HTTP headers (like User-Agent). You must manually set the User-Agent.
The best solution is to use only 1 User-Agent (it would be strange to have multiple User-Agents coming from 1 IP, isn’t it?).
Mode C: HTTPS over HTTP (or *no tunnel* mode)
This mode is for scraper. It allows Scrapoxy to override HTTP headers (like User-Agent).
The scraper must send a HTTP request with an HTTPS URL in the Location header.
Example:
GET /index.html
Host: localhost:8888
Location: https://www.google.com/index.html
Accept: text/html
Scrapers accept a GET (or POST) method instead of CONNECT for proxy.
With Scrapy (Python), add /?noconnect to the proxy URL:
PROXY='http://localhost:8888/?noconnect
With Request (Node.js), add tunnel:false to options:
request({
method: 'GET',
url: 'https://api.ipify.org/',
tunnel: false,
proxy: 'http://localhost:8888',
}, (err, response, body) => {...});
What is the proxy that returned the response ?
Scrapoxy adds to the response an HTTP header x-cache-proxyname.
This header contains the name of the proxy.
If you are using HTTPS in HTTPS CONNECT without MITM, Scrapoxy is unable to add this header since the traffic is encrypted.
Can the scraper force the request to go through a specific proxy?
Yes. The scraper adds the proxy name in the header x-cache-proxyname.
When the scraper receives a response, this header is extracted. The scraper adds this header to the next request.
Does Scrapoxy override User Agent ?
Yes. When an instance starts (or restarts), it gets a random User Agent (from the User Agent list).
When the instance receives a request, it overrides the User Agent.
Blacklisting
How can you manage blacklisted response ?
Remember, Scrapoxy cannot detect blacklisted response because it is too specific to a scraping usecase. It can be a 503 HTTP response, a captcha, a longer response, etc.
Anti-blacklisting is a job for the scraper:
The scraper must detect a blacklisted response;
The scraper extracts the name of the instance from the HTTP response header (see here);
The scraper asks to Scrapoxy to remove the instance with the API (see here).
When the blacklisted response is detected, Scrapoxy will replace the instance with a valid one (new IP address).
There is a tutorial: Manage blacklisted request with Scrapy.
Instances management
How does multi-providers work ?
In the configuration file, you can specify multiple providers (the providers field is an array).
You can also specify the maximum number of instances by provider, with the max parameter (for example: 2 instances maximum for AWSEC2 and unlimited for DigitalOcean).
When several instances are requested, the algorithm randomly asks the instances at the providers, within the specified capacities.
How does the monitoring mechanism ?
the manager asks the cloud how many instances are alive. It is the initial state;
the manager creates a target state, with the new count of instance;
the manager generates the commands to reach target state from the initial state;
the manager sends the commands to the cloud.
- These steps are very important because you cannot guess which is the initial state.
Because an instance may be dead!
Scrapoxy can restart an instance if:
the instance is dead (stop status or no ping);
the living limit is reached: Scrapoxy regulary restarts the instance to change the IP address.
Do you need to create a VM image ?
By default, we provide you an AMI proxy instance on AWS / EC2. This is a CONNECT proxy opened on TCP port 3128.
But you can use every software which accept the CONNECT method (Squid, Tinyproxy, etc.).
Can you leave Scrapoxy started ?
Yes. Scrapoxy has 2 modes: an awake mode and an asleep mode.
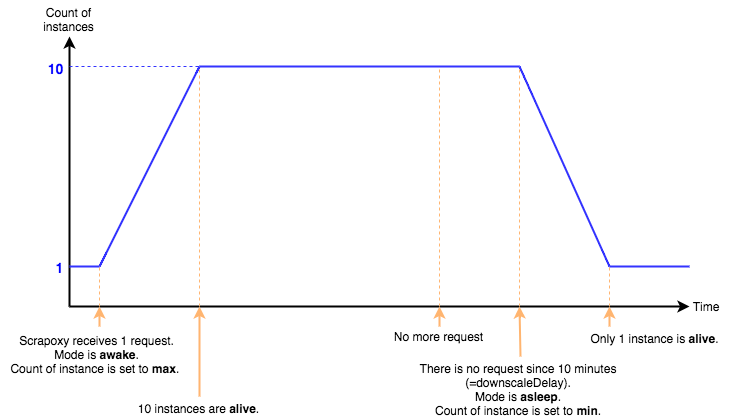
When Scrapoxy receives no request after a while, he falls asleep. It sets the count of instances to minimum (instance.scaling.min).
When Scrapoxy receives a request, it wakes up. It fixes the count of instances to maximum (instance.scaling.max).
Scrapoxy needs at least 1 instance to receive the awake request.